According to a CNBC article on cyber security trends, a 2019 CEO Imperative Study conducted by management consultancy EY reports that CEOs see cyber security as the number one threat […]


According to a CNBC article on cyber security trends, a 2019 CEO Imperative Study conducted by management consultancy EY reports that CEOs see cyber security as the number one threat […]

20 July 2019 marks the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 11 moon landing. Computers played a huge part in getting the Apollo 11 crew to the moon and back. In […]

Thanks to decreasing renewable energy prices and progressive policymakers, state-level 100% clean energy targets are becoming more common across the United States. Federal policymakers have proposed legislation that would mandate […]
A Professional Engineer (PE) license requires a four-year engineering degree, four or more years of progressive experience under a professional engineer (in most states), and a multidisciplinary understanding of physical […]

According to Gartner, a leading research and advisory company, blockchain has the potential to become a viable solution for major supply chain issues as the complexity of the supply chain […]

The global water crisis is causing problems worldwide. The United Nations estimates that 2.1 billion people do not have access to safe drinking water in their homes. This is relevant […]

People are investing billions of dollars in autonomous vehicle (AV) technology. The industry is displaying spectacular advancements to show for it. However, we are still nowhere near achieving the widespread […]

The future promises dramatic transformations in the way people make and consume energy. Many experts are turning to microgrids— small-scale, self-sustaining power networks unburdened by ties to a centralized power […]
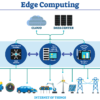
Depending on how many of the 30 billion Internet of Things (IoT) devices forecast for global deployment by 2020 rely on the cloud, managing the deluge of IoT-generated data makes […]
The current technologies used in the healthcare industry face limitations in areas security, privacy, and full ecosystem interoperability. Although several challenges must be addressed before any large scale adoption can […]
