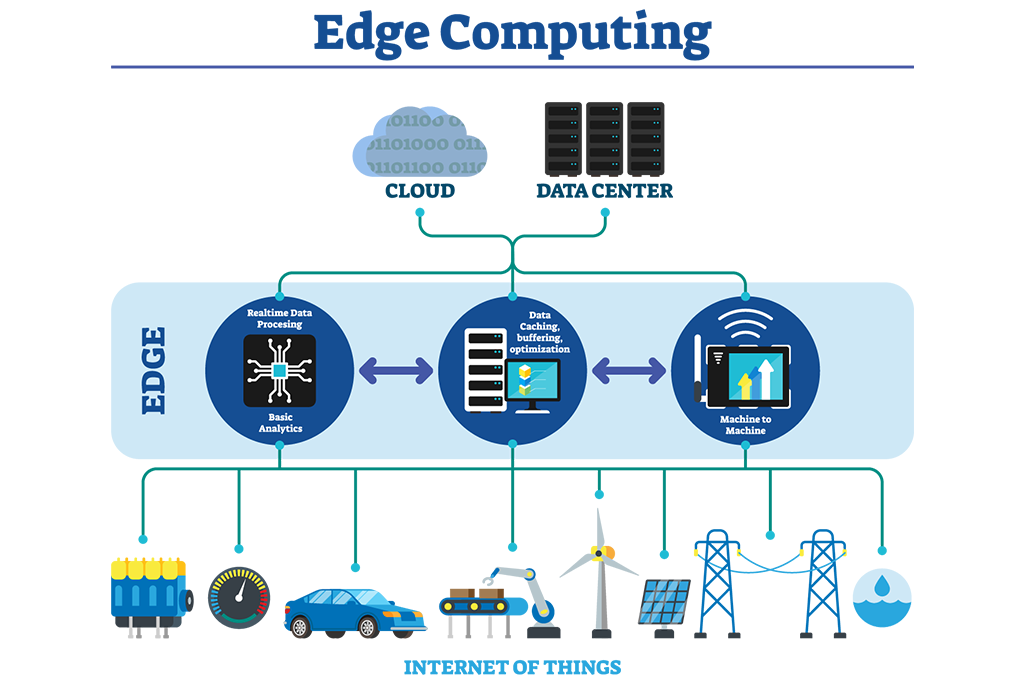
Depending on how many of the 30 billion Internet of Things (IoT) devices forecast for global deployment by 2020 rely on the cloud, managing the deluge of IoT-generated data makes proper processing seem near impossible. Traditional cloud computing has serious disadvantages, including data security threats, performance issues, and growing operational costs. Because most data saved in the cloud has little significance and is rarely used, it becomes a waste of resources and storage space.
In many instances, it would be incredibly beneficial to handle data on the device where it’s generated. That’s where edge computing comes in. Edge computing helps decentralize data processing and lower dependence on the cloud.
Edge computing has several advantages, such as:
-
- Increasing data security and privacy
- Better, more responsive and robust application performance
- Reducing operational costs
- Improving business efficiency and reliability
- Unlimited scalability
- Conserving network and computing resources
- Reducing latency
Edge Computing Use Cases
Prime use cases, which take full advantage of edge technology, include:
Autonomous Vehicles: The decision to stop for a pedestrian crossing in front of an autonomous vehicle (AV) must be made immediately. Relying on a remote server to handle this decision is not reasonable. Additionally, vehicles that utilize edge technology can interact more efficiently because they can communicate with each other first as opposed to sending data on accidents, weather conditions, traffic, or detours to a remote server first. Edge computing can help.
Healthcare Devices: Health monitors and other wearable healthcare devices can keep an eye on chronic conditions for patients. It can save lives by instantly alerting caregivers when help is required. Additionally, robots assisting in surgery must be able to quickly analyze data in order to assist safely, quickly, and accurately. If these devices rely on transmitting data to the cloud before making decisions, the results could be fatal.
Security Solutions: Because it’s necessary to respond to threats within seconds, security surveillance systems can also benefit from edge computing technology. Security systems can identify potential threats and alert users to unusual activity in real-time.
Retail Advertising: Targeted ads and information for retail organizations are based on key parameters, such as demographic information, set on field devices. In this use case, edge computing can help protect user privacy. It can encrypt the data and keep the source rather than sending unprotected information to the cloud.
Smart Speakers: Smart speakers can gain the ability to interpret voice instructions locally in order to run basic commands. Turning lights on or off, or adjusting thermostat settings, even if internet connectivity fails would be possible.
Video Conferencing: Poor video quality, voice delays, frozen screens— a slow link to the cloud can cause many video conferencing frustrations. By placing the server-side of video conferencing software closer to participants, quality problems can be reduced.
Further Enhanced Security
Although edge computing is a sensible alternative to cloud computing in many instances, there’s always room for improvement. According to “Reconfigurable Security: Edge Computing-Based Framework for IoT”, a paper published by IEEE Network, existing IoT security protocols need improvement.
A possible solution to better secure IoT-generated data is an IoT management element called the Security Agent. This new piece would use routers and other near-edge boxes to manage the computing the IoT device could not take on. In addition to being more secure, it’ll simplify the management of keys. The Security Agent box has the capability of running copious sensors that are difficult to access. The researchers’ state that if the needed authentification is not completed quickly, IoT applications will fail.
Getting Up to Speed
Designed for organizations investing heavily in this critical technology, IEEE Introduction to Edge Computing is a five-course program designed to train your entire team to support edge computing. The online, on-demand courses included in this program are:
- Overview of Edge Computing
- Practical Applications of Edge Computing
- Research Challenges in Edge Computing
- Designing Security Solutions for Edge, Cloud, and IoT
- Tools and Software for Edge Computing Applications
To learn more about getting access to these courses for your organization, connect with an IEEE Content Specialist today.
Resources
Aleksandrova, Mary. (1 Feb 2019). The Impact of Edge Computing on IoT: The Main Benefits and Real-Life Use Cases. Eastern Peak.
Nelson, Patrick. (10 Jan 2019). How edge computing can help secure the IoT. Network World.
Caulfield, Matt. (23 Oct 2018). Edge Computing: 9 Killer Use Cases for Now & the Future. Medium.
Talluri, Raj. (24 Oct 2017). Why edge computing is critical for the IoT. Network World.


Can’t wait. Very exciting times ahead!